Page 28 - Kindergarten.indd
P. 28
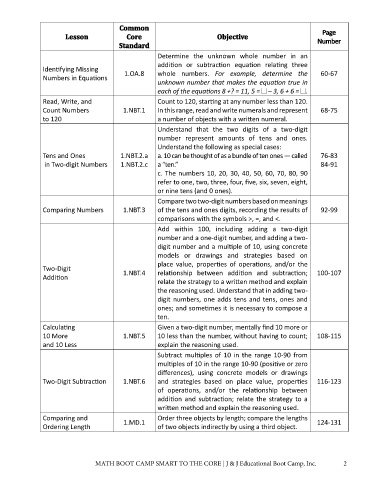
Common
Lesson Core Objective Page
Standard Number
Determine the unknown whole number in an
addition or subtraction equation relating three
Identifying Missing
Numbers in Equations 1.OA.8 whole numbers. For example, determine the 60-67
unknown number that makes the equation true in
each of the equations 8 +? = 11, 5 = – 3, 6 + 6 = .
Read, Write, and Count to 120, starting at any number less than 120.
Count Numbers 1.NBT.1 In this range, read and write numerals and represent 68-75
to 120 a number of objects with a written numeral.
Understand that the two digits of a two-digit
number represent amounts of tens and ones.
Understand the following as special cases:
Tens and Ones 1.NBT.2.a a. 10 can be thought of as a bundle of ten ones — called 76-83
in Two-digit Numbers 1.NBT.2.c a “ten.” 84-91
c. The numbers 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90
refer to one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight,
or nine tens (and 0 ones).
Compare two two-digit numbers based on meanings
Comparing Numbers 1.NBT.3 of the tens and ones digits, recording the results of 92-99
comparisons with the symbols >, =, and <.
Add within 100, including adding a two-digit
number and a one-digit number, and adding a two-
digit number and a multiple of 10, using concrete
models or drawings and strategies based on
place value, properties of operations, and/or the
Two-Digit
Addition 1.NBT.4 relationship between addition and subtraction; 100-107
relate the strategy to a written method and explain
the reasoning used. Understand that in adding two-
digit numbers, one adds tens and tens, ones and
ones; and sometimes it is necessary to compose a
ten.
Calculating Given a two-digit number, mentally find 10 more or
10 More 1.NBT.5 10 less than the number, without having to count; 108-115
and 10 Less explain the reasoning used.
Subtract multiples of 10 in the range 10-90 from
multiples of 10 in the range 10-90 (positive or zero
differences), using concrete models or drawings
Two-Digit Subtraction 1.NBT.6 and strategies based on place value, properties 116-123
of operations, and/or the relationship between
addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a
written method and explain the reasoning used.
Comparing and 1.MD.1 Order three objects by length; compare the lengths 124-131
Ordering Length of two objects indirectly by using a third object.
MATH BOOT CAMP SMART TO THE CORE | J & J Educational Boot Camp, Inc. 2