Page 3 - Kindergarten.indd
P. 3
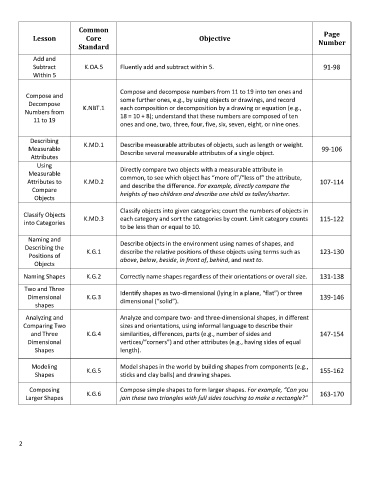
Common
Page
Lesson Core Objective Number
Standard
Add and
Subtract K.OA.5 Fluently add and subtract within 5. 91-98
Within 5
Compose and decompose numbers from 11 to 19 into ten ones and
Compose and some further ones, e.g., by using objects or drawings, and record
Decompose
Numbers from K.NBT.1 each composition or decomposition by a drawing or equation (e.g.,
18 = 10 + 8); understand that these numbers are composed of ten
11 to 19
ones and one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, or nine ones.
Describing K.MD.1 Describe measurable attributes of objects, such as length or weight.
Measurable Describe several measurable attributes of a single object. 99-106
Attributes
Using
Measurable Directly compare two objects with a measurable attribute in
Attributes to K.MD.2 common, to see which object has “more of”/“less of” the attribute, 107-114
and describe the difference. For example, directly compare the
Compare
Objects heights of two children and describe one child as taller/shorter.
Classify objects into given categories; count the numbers of objects in
Classify Objects K.MD.3 each category and sort the categories by count. Limit category counts 115-122
into Categories
to be less than or equal to 10.
Naming and Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes, and
Describing the K.G.1 describe the relative positions of these objects using terms such as 123-130
Positions of above, below, beside, in front of, behind, and next to.
Objects
Naming Shapes K.G.2 Correctly name shapes regardless of their orientations or overall size. 131-138
Two and Three Identify shapes as two-dimensional (lying in a plane, “flat”) or three
Dimensional K.G.3 dimensional (“solid”). 139-146
shapes
Analyzing and Analyze and compare two- and three-dimensional shapes, in different
Comparing Two sizes and orientations, using informal language to describe their
and Three K.G.4 similarities, differences, parts (e.g., number of sides and 147-154
Dimensional vertices/“corners”) and other attributes (e.g., having sides of equal
Shapes length).
Modeling K.G.5 Model shapes in the world by building shapes from components (e.g., 155-162
Shapes sticks and clay balls) and drawing shapes.
Composing K.G.6 Compose simple shapes to form larger shapes. For example, “Can you 163-170
Larger Shapes join these two triangles with full sides touching to make a rectangle?”
2